The AI Coding Reality Check
Understanding the Security Risks
Welcome to the future of software development — or is it? If you've spent any time around developers lately, you've probably heard the buzz about AI coding assistants. GitHub Copilot, Amazon CodeWhisperer, Cursor, ChatGPT, Claude — these tools have exploded onto the scene and fundamentally changed how code gets written.
But before we dive into the security challenges (trust us, there are plenty), let's understand what we're dealing with and why these tools have become so incredibly popular so quickly.
AI coding assistants are tools powered by large language models (LLMs) that help developers write code. They work by analyzing billions of lines of code from public repositories and learning patterns, syntax, and common solutions to programming problems.
Think of them as an incredibly knowledgeable pair programmer who's read almost every public codebase on the internet. When you start typing code, they suggest completions. When you describe what you want in plain English, they generate entire functions. When you're stuck on a bug, they can explain unfamiliar code or suggest fixes.
The main players include:
Each tool has its own strengths, pricing models, and privacy policies (more on that later), but they all share a common promise: write better code, faster.
The adoption of AI coding tools has been nothing short of remarkable. Following GitHub Copilot’s launch in 2021, adoption grew rapidly, with millions of developers trying these tools within the first couple of years.
By 2025, AI coding assistants are widely used across many software organizations globally 1 2.
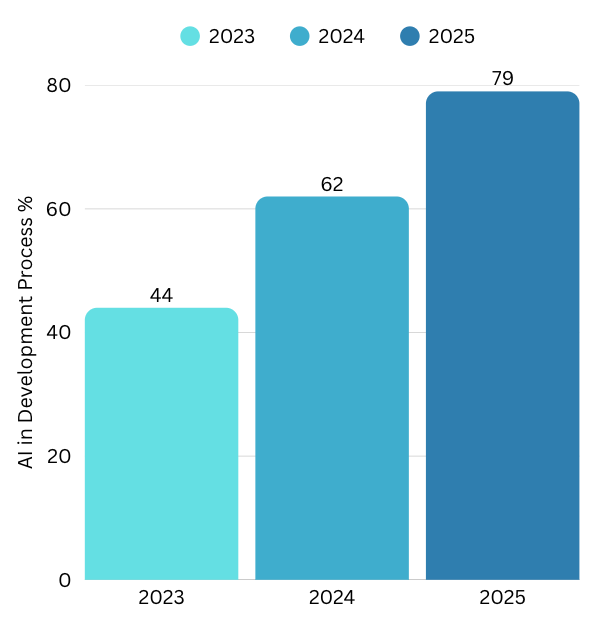 AI tools in the development process - StackOverflow Developer Survey 7 8 9
AI tools in the development process - StackOverflow Developer Survey 7 8 9
Why the explosive growth? A few key factors:
Developer demand: Many developers discovered these tools organically, tried them, loved them, and spread the word. Adoption has often been grassroots, later supported by enterprise rollouts 2.
Immediate value: Unlike many enterprise tools that require weeks of training, AI assistants provide value within minutes of installation. The feedback loop is instant.
The remote work era: With distributed teams and knowledge silos, having an AI assistant that can explain unfamiliar code became incredibly valuable.
Competitive pressure: Once some developers started using AI, others felt pressure to keep up. Teams worried about falling behind if they didn’t adopt similar tools 2 3.
Let’s be honest about the benefits — they’re real, and they’re significant. Understanding why developers love these tools helps us build realistic policies later.
1. Speed on Boilerplate Code
One of the biggest time-sinks in development is writing repetitive, predictable code. Setting up a REST API endpoint? Configuring a database connection? Writing test fixtures? AI assistants excel at this.
Some organizations report productivity gains of up to 50% on routine tasks when using AI-generated code, particularly for boilerplate or repetitive work 3 6.
2. Explaining Unfamiliar Codebases
Ever joined a new team and spent weeks trying to understand the existing codebase? AI assistants can read through thousands of lines of code and explain what it does in plain English. They can trace function calls, explain complex algorithms, and help new team members get up to speed faster.
3. Suggesting Complex Algorithms
Need to implement a sorting algorithm? Parse a complex data structure? Generate regex patterns? AI assistants can suggest implementations based on patterns they’ve learned from millions of examples.
4. Reduced Cognitive Load
Writing code isn’t just about typing — it’s about holding complex logic in your head while simultaneously remembering syntax, library names, and API signatures. AI assistants handle the syntax and API details, letting developers focus on business logic 3.
Reducing this cognitive load helps developers work more efficiently and may reduce common errors in repetitive or boilerplate code.
5. Learning and Exploration
Junior developers use AI assistants as learning tools. Instead of searching Stack Overflow for hours, they can ask the AI to explain concepts, show examples, and suggest best practices. It’s like having a senior developer available 24/7.
Developers didn’t adopt these tools because of marketing — they adopted them because of real, tangible wins:
The autocomplete that actually understands context: Unlike traditional IDE autocomplete, AI suggestions understand what you’re trying to do based on your function names, comments, and surrounding code.
The “write tests for this function” command: Generating unit tests is tedious and time-consuming. AI can scaffold tests in seconds.
The code translator: Need to convert Python to JavaScript? Rewrite legacy code in a modern framework? AI can handle the grunt work 3.
The documentation generator: Good documentation is important but painful to write. AI can generate initial drafts from code, which developers can then refine.
The stack trace analyzer: When you hit a cryptic error, AI can explain what went wrong and suggest fixes based on similar issues it has seen before.
The numbers tell the story:
This isn’t a fad — it’s a fundamental shift in how software gets written.
AI has introduced a new paradigm where developers focus less on writing every line by hand and more on guiding AI to generate and refine code through prompts and iteration.
This “vibe coding” culture reflects a shift toward higher-level reasoning and creative direction over manual syntax. Some developers embrace it enthusiastically, while others — especially in security and compliance — remain cautious 2.
This cultural divide is something every organization must navigate.
If you’re reading this course, you’re probably responsible for managing this shift in your organization. Here’s why understanding the appeal matters:
You can’t fight demand: Developers want these tools. Banning them creates frustration and often drives unofficial usage 2.
The benefits are real: Dismissing AI tools as “just hype” ignores legitimate productivity gains 3 6.
But so are the risks: The same factors that make these tools powerful also make them dangerous when used without guardrails.
Your job isn’t to stop AI adoption — it’s to enable it safely.
Now that you understand why AI coding assistants have taken over the development world, we need to talk about the other side of the coin. In the next chapter, we’ll explore the dark side — the security vulnerabilities, data leaks, and false assumptions that come with AI-generated code.
Spoiler alert: research shows that around half of AI-generated code samples in academic studies contain vulnerabilities, and most developers don’t realize it 4 5.
Before moving on, make sure you understand:
[1] TechCrunch (2025) – GitHub Copilot crosses 20 million all-time users
[2] Infolia AI (2025) – The real state of AI coding assistant adoption in 2025
[3] Second Talent (2024) – AI Coding Assistant Statistics and Market Forecast
[4] arXiv (2024) – The Security Risks of AI-Generated Code (2404.18353)
[5] arXiv (2023) – Empirical Study of Security Vulnerabilities in AI-Generated Code (2310.02059)
[6] Publicis Sapient (2024) – Internal productivity reports (not publicly available; cited in industry summaries)
[7] StackOverflow – Developer Survey 2023
[8] StackOverflow – Developer Survey 2024
[9] StackOverflow – Developer Survey 2025
Mark this chapter as finished to continue
Mark this chapter as finished to continue