Fundamentals
Invisible AI
Conversational AI
Now that you've got a basic understanding of LLMs and how they serve as an API we can dive into the secret sauce - how to actually speak the language of these models to get the results that you want.
You do this using prompts.
Prompts are the text input that you send to the LLM. Prompting can be powerful, but requires effective techniques to get consistent results. An LLM will respond to any prompt, but all prompts are not created equally.
Good prompts can turn an LLM from novelty into a reliable coworker.
Think of prompting a model like a chef preparing a meal. Bad ingredients will result in a bad meal.
Same with AI: bad prompt = bad output, no matter how fancy your code wrapper.
A good prompt is crucial. It's what gets the AI to consistently do what you want.
🔄 The Golden Rule of Prompting
Iterate aggressively. Monitor outputs. Keep tweaking.
Before diving into techniques, understand the basic anatomy of a good prompt:
Basic Prompt Structure (ICOD). Good prompts typically contain:
- Instruction: What task to do
- Context: Background info
- Output Indicator: Format requirements (critical for
generateObject)- Data: The actual input
Let's dive into three core techniques every builder needs to know:
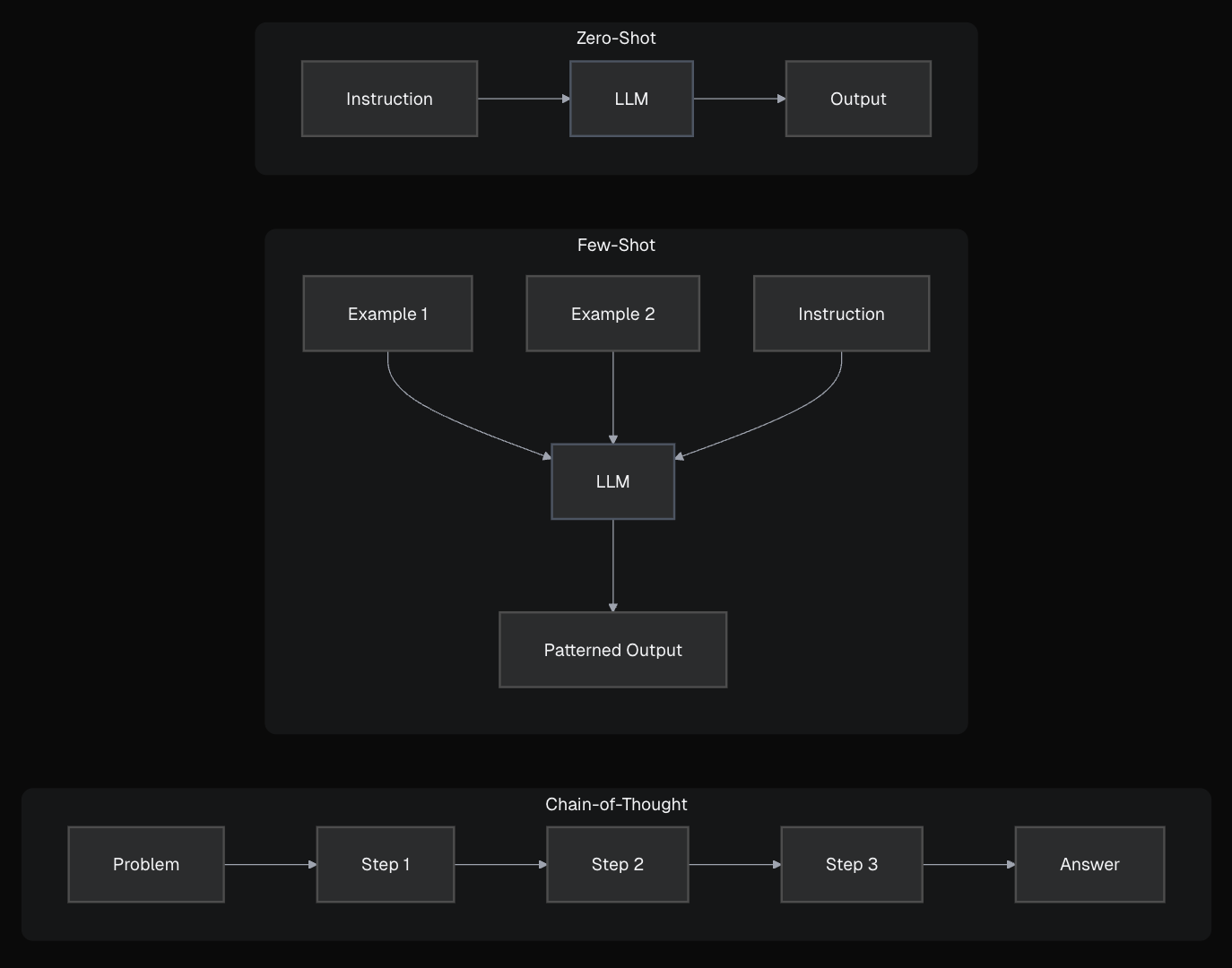
This is the simplest and most common form of prompting: simply asking the model to do something directly, without providing examples.
Classify the sentiment (positive/negative/neutral): 'This movie was okay.'NeutralgenerateText calls where the task is common (like basic summarization, Q&A). Relies heavily on the model's pre-trained knowledge.javascript
This approach is great for quick for straightforward tasks, but less reliable for complex instructions or specific output formats.
For more complex tasks or specific output formats, you need to provide examples within the prompt to show the model the pattern or format you want it to follow.
text
The model sees the pattern (definition → example) and completes it. This structured approach uses our ICOD framework:
ICOD Breakdown for Few-Shot Example
javascript
Providing examples massively improves reliability for specific formats. Clear labels and consistent formatting in examples are key!
Mimic human problem-solving by prompting the model to "think out loud" and break down a complex task into intermediate reasoning steps before giving the final answer.
text
Here's how you would use this style of prompt with the AI SDK:
javascript
Showing the model "how to think" about the problem improves reliability for logic and complex reasoning. Combine this with few-shot. Remember that this technique often performs best with more capable models.
Remember this crucial advice:

Don't leave the model wondering what to do with its hands!
Before setting up your local environment, let's practice these prompting techniques using the AI SDK Playground. This web-based tool lets you experiment with prompts immediately - no setup required!
The playground allows you to:
Why This Practice Matters
- The AI SDK Playground lets you experiment with prompting techniques immediately. You're learning patterns that will power the
generateObjectandgenerateTextcalls you'll build in upcoming lessons.- Key insight: Good prompts + structured schemas = reliable AI features in your applications!
Open the AI SDK Playground and try this Few-Shot example:
Prompt to try:
text
What to observe:
In the playground, test this Chain-of-Thought prompt:
Prompt to try:
text
What to observe:
Switch to structured output mode in the playground and test this schema:
Schema:
text
Prompt: "Analyze this user feedback: 'Love the new search feature, but it's a bit slow when I type fast.'"
Prompt engineering is a vast, complex, and ever-evolving topic. Here are some resources to help you dive deeper:
artifacts/.../server.ts files!You've grasped the core prompting techniques and practiced implementing them with the AI SDK. Now it's time to prepare your local machine and set up your development environment with the necessary tools and API keys.
The best way to solidify your prompting skills is by building real stuff. Let's get your environment ready so you can go from talking about prompts to implementing them in working code.
Mark this chapter as finished to continue
Mark this chapter as finished to continue