Not all AI models are created equal. Some prioritize speed for real-time interactions, while others take time to think through complex problems. Understanding these differences is crucial for building great user experiences.
In this lesson, you'll learn about the two main categories of models, fast and reasoning models, and when to use each.
Project Context
We'll compare different model types using simple examples to understand their trade-offs. This knowledge will guide your model choices throughout the course.
The AI SDK gives you access to different types of models, each optimized for different use cases:
Characteristics:
- Start responding immediately (< 1 second)
- Stream tokens as they're generated
- Great for real-time interactions
- Lower cost per token
- Best for straightforward tasks
Best for:
- Chatbots and conversational interfaces
- Quick content generation
- Simple question answering
- Real-time assistance
Characteristics:
- Think before responding (5-15+ seconds)
- More thorough problem analysis
- Better at complex reasoning tasks
- Higher cost per token
- Best for difficult problems
Best for:
- Complex problem solving
- Mathematical reasoning
- Code analysis and debugging
- Multi-step logical tasks
- Research and analysis
Let's create a practical script to experience the differences between fast and reasoning models:
Create model-comparison.ts in your project root:
Replace the first TODO with:
Replace the second TODO with:
Replace the third TODO with:
Uncomment the function call and run:
What You'll Experience:
- Fast model: ~1-3 seconds, streams response immediately
- Reasoning model: ~10-15 seconds delay, then faster output
Real-World Application
This timing difference directly impacts user experience:
- Fast models: Perfect for chat interfaces where users expect immediate responses
- Reasoning models: Better for complex analysis where users can wait for higher quality results
Your model choice should match user expectations and use case requirements!
Typical Results:
- Fast model: ~1-3 seconds, good answer
- Reasoning model: ~10-15 seconds, more thorough analysis
Here's a decision framework:
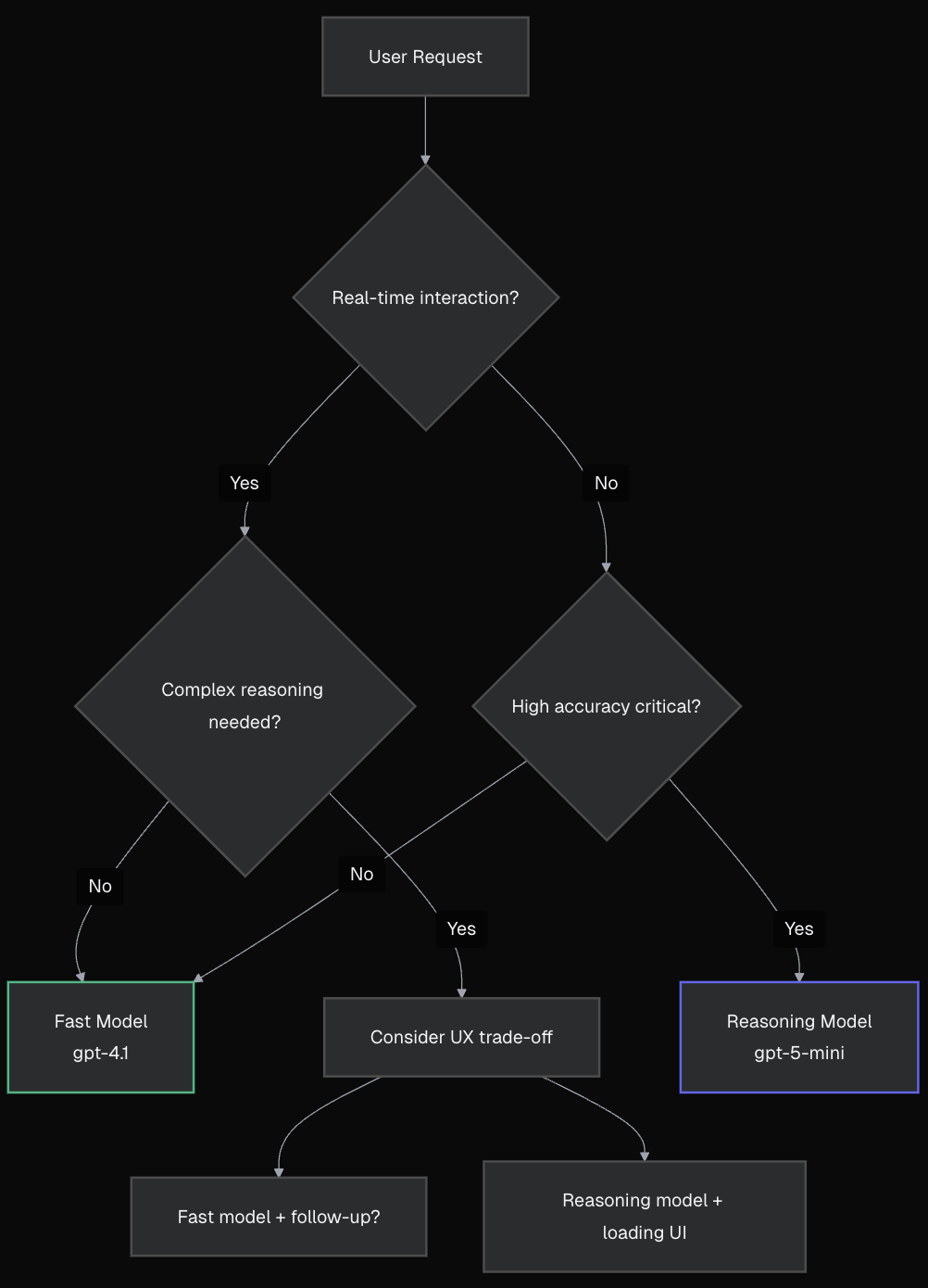
- Building chatbots or conversational UI
- Users expect immediate responses
- Tasks are straightforward
- Streaming responses improve UX
- Cost efficiency is important
- Complex problem-solving is required
- Accuracy is more important than speed
- Users can wait for better results
- The task benefits from "thinking time"
- You can provide good loading states
- Start with fast model for immediate response
- Offer "detailed analysis" with reasoning model
- Use fast model for chat, reasoning for reports
- Let users choose based on their needs
Fast Models:
Reasoning Models:
For Reasoning Models:
- Show thinking/loading indicators
- Set proper expectations ("This might take 10-15 seconds")
- Consider progressive disclosure
- Provide cancel options for long requests
For Fast Models:
- Embrace real-time streaming
- Keep interfaces responsive
- Handle quick back-and-forth conversations
Reasoning models typically cost more per token due to their computational requirements:
- Fast models: Lower cost, faster throughput
- Reasoning models: Higher cost, better quality for complex tasks
Factor this into your application's economics, especially for high-volume use cases.
When using reasoning models that take time to think, consider these UX patterns:
Loading States:
- Show clear indicators that the AI is thinking
- Provide time estimates ("This might take 10-15 seconds")
- Consider progress indicators for long operations
Transparency:
- Explain why the delay is happening
- Show the AI's reasoning process when appropriate
- Let users know they're getting higher quality results
User Control:
- Provide cancel options for long-running requests
- Let users choose between fast and thorough responses
- Remember user preferences for future interactions
- Fast model for product questions, order status
- Reasoning model for complex return policies, compatibility analysis
- Loading states while reasoning model analyzes recommendations
- Fast model for autocomplete, quick explanations
- Reasoning model for debugging, architecture reviews
- Progress indicators during complex code analysis
- Fast model for casual Q&A, definitions
- Reasoning model for solving math problems, essay analysis
- Step-by-step display of problem-solving process
- Model Types: Fast vs reasoning models serve different purposes
- Trade-offs: Speed vs thoroughness, cost vs quality
- Selection Criteria: Match model type to use case and user expectations
- UX Considerations: How model choice affects interface design
- Cost Factors: Balance performance needs with budget constraints
Understanding these model characteristics will help you make informed decisions throughout the rest of the course. In the next section, we'll explore "invisible AI" techniques where model choice significantly impacts user experience.
You've learned the fundamentals - now it's time to build features users will love! In the next section, you'll discover how to:
🎯 Transform Text into Structured Data:
- Use
generateObject with Zod schemas for reliable, typed results
- Build smart categorization that sorts support tickets automatically
- Create extraction features like calendar event parsing from natural language
⚡ Choose the Right Model for the Job:
- Fast models (
openai/gpt-4.1) for real-time classification and extraction
- Reasoning models (
openai/gpt-5-mini) for complex analysis and summarization
- Learn when speed vs accuracy matters for user experience
🔧 Practical Patterns You'll Build:
- Text Classification: Automatically categorize user feedback, emails, or support requests
- Smart Summarization: Turn long threads into concise, actionable summaries
- Data Extraction: Parse natural language into structured calendar events, contacts, or forms
These "invisible AI" features work behind the scenes to make your app feel magical - users get better experiences without realizing AI is helping!
Now that you understand model types, you're ready to explore invisible AI - AI that works behind the scenes to enhance user experiences without requiring direct interaction.
